5 Things You Should Know
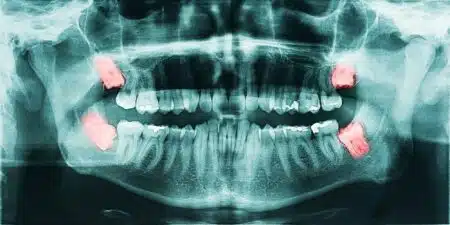
- What are wisdom teeth?
The third permanent molars, or better known as the wisdom teeth, are a set of four teeth. Majority of adults develop these teeth, though in some are congenitally missing. These teeth are typically the smallest of the molars and are located in very back of the mouth. They typically grow into occlusion between the ages of 17-21 years of age.
- How do I know if I have wisdom teeth?
Around ages 5-6 or older the Pediatric Dentist on the floor will most likely order a panoramic radiograph. This diagnostic image allows the clinician to see everything from the orbital sockets to the bottom of the chin. By age 9, this includes the third molars. Which is a lot! This much information is not seen in the routine bitewings or periapical radiographs which, in contrast, are used to detect cavities and other radiographic lesions.
- Why do people get wisdom teeth removed?
In the past it was common practice to have all wisdom teeth extracted. Now in days, they are only to be extracted if:
- There is not enough space to properly erupt
- They are prone to misalignment
- They are growing into adjacent teeth
- They are causing infection, sharp pain, and/or cavities
- What happens if I am told that I need them extracted?
Upon recommendation it is imperative to follow through with the treatment plan. Some dentists are able to remove the wisdom teeth in-office due to complexity. Some wisdom teeth may be more difficult to access which is why a referral to an Oral Surgeon may be indicated. Pediatric dentists usually do not perform these procedures. It is important to follow the dentist’s pre and post-procedural instructions to ensure a proactive and efficient recovery.
- What happens if I do not get my wisdom teeth extracted as recommended?
Large cysts may form and resorb healthy bone before the tooth erupts. Sharp, spontaneous, yet consistent pain may interfere throughout your everyday life if the tooth pushes into a neighboring tooth. If the wisdom tooth is partially erupted, plaque or tartar that cannot be cleaned routinely which may result in dental caries or periodontal disease.